Signing Made Simple: A Guide to 3 Types of Electronic Signatures
2024-04-18 14:00:40 • Filed to: Software for Business • Proven solutions
In the fast-paced world of modern business, electronic signatures are essential. They simplify transactions and save time by eliminating paperwork. These digital signatures are legally recognized and binding. Thus, ensuring security in a paperless environment.
In this guide, we'll explore the three (3) types of electronic signatures and their significance. They can help you to make informed decisions for seamless signing experiences. Embrace the convenience and efficiency of electronic signatures in your business endeavors.

Part 1. Wet Signatures, Digital Signatures, and Electronic Signatures
Three main types stand out in the signatures world: wet, digital, and electronic.
- Wet Signatures: Wet or traditional signatures involve physically signing a document with ink on paper. However, wet signatures present limitations in the digital age as they require face-to-face interactions or mailing, causing delays and inefficiencies.
- Digital Signatures: Digital signatures, on the other hand, offer a more advanced solution. They use cryptographic algorithms to ensure data integrity and authenticity. When a document is digitally signed, it creates a unique fingerprint that verifies if any changes have been made to the content.
- Electronic Signatures: Electronic signatures go beyond wet and digital signatures, revolutionizing the signing process. They offer numerous advantages, such as quick turnaround times, reduced costs, and eco-friendliness by eliminating paper usage.
Unlike wet signatures, electronic signatures enable remote signing, making them ideal for businesses with a global reach or those that rely on telecommuting. They are also more secure than traditional wet signatures, providing audit trails and encryption to protect sensitive information.
While digital signatures provide enhanced security, they may require specific software or infrastructure, limiting accessibility for some users. In contrast, electronic signatures offer a user-friendly experience accessible from various devices.
Different types of electronic signatures cater to varying business needs. Basic electronic signatures are suitable for simple transactions, while advanced electronic signatures, incorporating additional security measures, are used for more sensitive documents.
Electronic signatures have transformed how businesses handle documents, providing efficiency, security, and convenience. By understanding the distinctions between wet, digital, and electronic signatures, businesses can adopt the most suitable signing method for their unique requirements.
Part 2. The Three Types of Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures come in three distinct types, each with its features and level of security. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for making informed decisions when incorporating them into your business processes. Explore each type to see how they can streamline your signing procedures and enhance overall efficiency.
Basic Electronic Signatures
Basic electronic signatures, also known as standard electronic signatures or simple e-signatures, are the most straightforward type of digital signatures. They capture a person's intent to sign a document electronically, typically by typing their name or selecting an "I agree" checkbox.
These signatures are commonly used in various industries and for various documents, including contracts, agreements, consent forms, and internal company documents. They provide a practical and convenient solution for routine tasks, simplifying the signing process for businesses and individuals.
While basic electronic signatures offer convenience, they might have some limitations concerning security compared to other electronic signature types. However, they are still legally binding in many jurisdictions, especially when the signer's identity and intent can be reasonably authenticated.
To enhance the security of basic electronic signatures, businesses can implement additional authentication measures, such as using unique login credentials or capturing the signer's IP address and geolocation. Furthermore, compliance with relevant regulations, like the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act in the United States or the eIDAS regulation in the European Union, is essential to ensure the validity of basic electronic signatures.
Basic electronic signatures offer a practical solution for everyday document signing needs, making them popular across diverse industries. However, exploring other electronic signatures might be necessary for more sensitive documents or situations requiring higher security.
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) provide higher security and reliability than basic electronic signatures. AES employs advanced cryptographic techniques to uniquely link the signature to the signer, ensuring integrity and non-repudiation.
AES uses various authentication methods like biometrics, smart cards, or digital certificates, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access or forge signatures. This heightened security makes AES ideal for critical documents, such as legal contracts, financial transactions, and sensitive agreements.
AES is widely adopted in industries like healthcare and finance, where confidentiality and data integrity are paramount. For instance, AES secures patient consent forms and medical records in the healthcare sector, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Despite its robustness, AES is not entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Risks include the compromise of private keys or stolen authentication devices. Strong key management practices, regular security audits, and multi-factor authentication are recommended to mitigate these risks.
Choosing AES over basic electronic signatures depends on the document's sensitivity and the level of security required. By leveraging AES, organizations can bolster the trustworthiness of their digital transactions, safeguarding against potential threats and fraudulent activities.
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) represent the highest level of electronic signature security. They meet stringent requirements defined by specific regulations, ensuring the signer's identity and the document's integrity.
To qualify as a QES, electronic signatures must be created using a secure digital certificate issued by a government-approved certification authority. The certificate uniquely identifies the signer, and tampering attempts are immediately detectable.
In various regions, QES holds legal validity equivalent to handwritten signatures, providing a robust and recognized digital signing solution. It is commonly used in sectors like finance, government, and legal, where compliance with strict regulations is essential.
In industries dealing with high-value transactions or sensitive data, such as real estate transactions, intellectual property agreements, and tax-related documents, QES is often mandated by law to ensure authenticity and non-repudiation.
When the highest level of signature security and legal compliance is required, QES is the most appropriate choice. It offers unmatched trustworthiness. Thus, making it the preferred option for critical documents and transactions. That demands the utmost integrity and regulatory adherence.
Part 3. Comparison of 3 Different Types of Electronic Signatures
The table below highlights the three main types of electronic signatures. Each type offers distinct features, security aspects, and legal validity.
|
Parameter
|
Basic Electronic Signatures
|
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
|
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simple, capturing signer's intent electronically, e.g., typing a name. | Enhanced security with cryptographic techniques, ensuring non-repudiation. | Highest level of security, meeting specific regulatory requirements. |
| Security Aspects | Moderate, authentication methods can be added but not mandated. | High, uses digital certificates, biometrics, or smart cards for robust authentication. | Very High, relies on government-approved certification authorities for digital certificates. |
| Legal Validity | Generally recognized and legally binding in many jurisdictions. | Widely recognized as legally valid in various regions. | Holds the highest level of legal validity, equivalent to handwritten signatures. |
| Use Cases | Routine agreements, consent forms, internal documents. | Critical contracts, financial transactions, healthcare records. | High-value transactions, legal agreements, government documents. |
- Definition: This outlines the fundamental nature of each signature type. Basic electronic signatures are the simplest and easiest to implement. On the other hand, QES has the highest level of security and regulatory compliance.
- Security Aspects: It is crucial to evaluate the level of protection each signature type offers. AES and QES provide higher security levels. They provide it through advanced cryptographic techniques and digital certificates. Thus, making them more suitable for critical documents.
- Legal Validity: Understanding the legal recognition of electronic signatures is essential. This is to ensure compliance with regional regulations. All three types hold legal validity. QES is the most recognized and equal to handwritten signatures in various jurisdictions.
- Use Cases: Identifying the appropriate use cases for each type is essential in making informed decisions. Basic electronic signatures are suitable for routine documents. AES and QES are preferred for critical transactions and sensitive agreements.
For standard and routine document signing needs, Basic Electronic Signatures are convenient. Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) suit finance, healthcare, and government sectors. Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are the best choice for the highest level of legal validity, especially in high-value transactions and compliance-driven industries.
Part 4. PDFelement: A Versatile Electronic Signature Solution
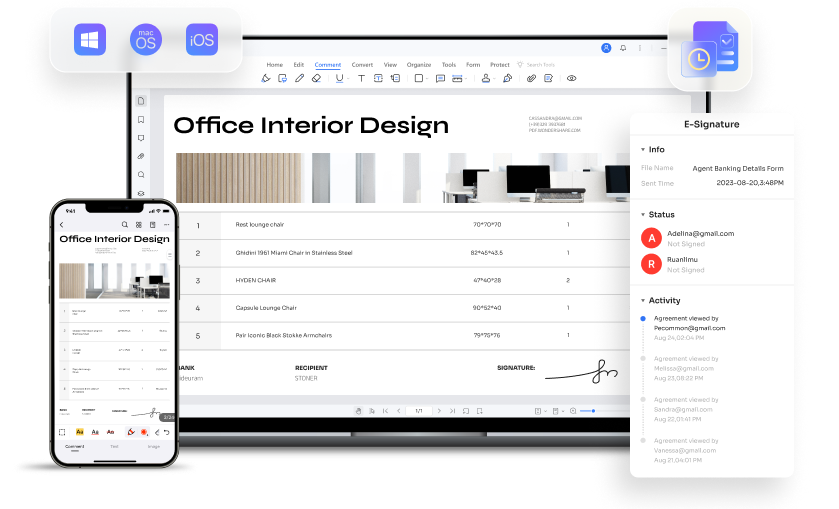
PDFelement is a versatile and comprehensive document management tool. It offers an efficient eSign feature, making it an ideal electronic signature solution. PDFelement simplifies the signing process for businesses of all sizes.
The eSign feature provided by PDFelement allows users to easily sign documents electronically. Whether it's a Basic Electronic Signature for routine agreements or an Advanced or Qualified Electronic Signature for more critical transactions, PDFelement caters to diverse signature needs.
Here's how to sign your document using PDFelement:
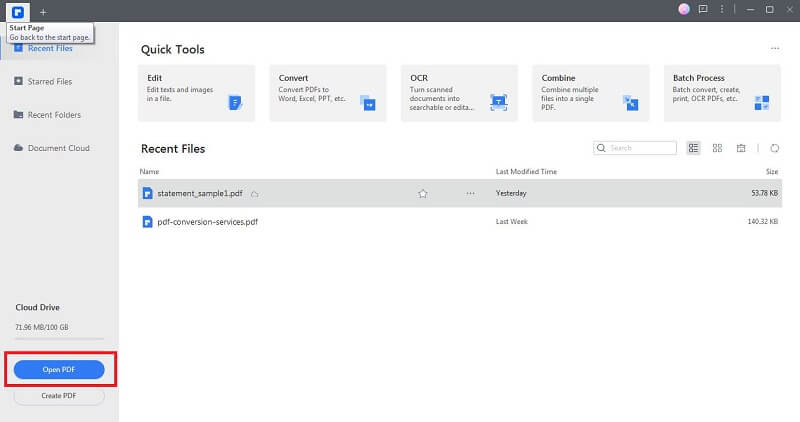
Step 1. Launch PDFelement and open the document by clicking "Open PDF."
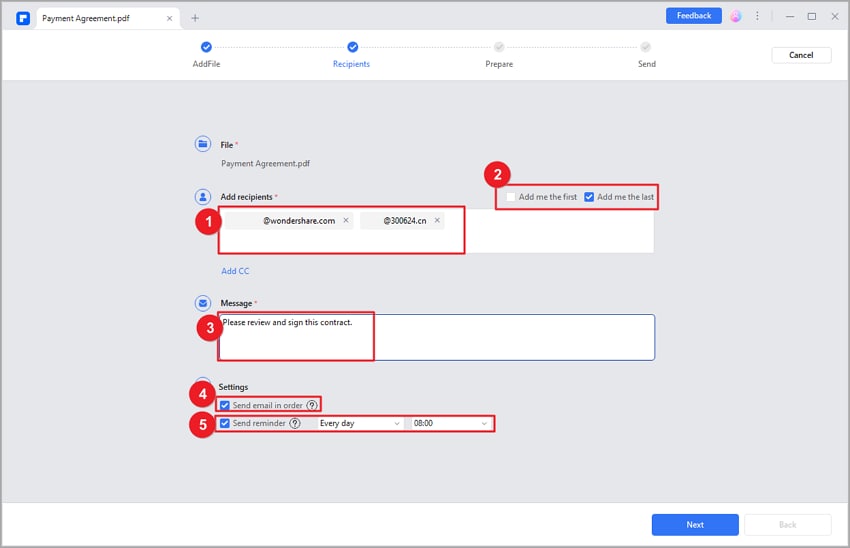
Step 2. Input recipient emails and set signing order.
- In your PDF, go to Protect > Request eSign. Input emails and arrange signing order.
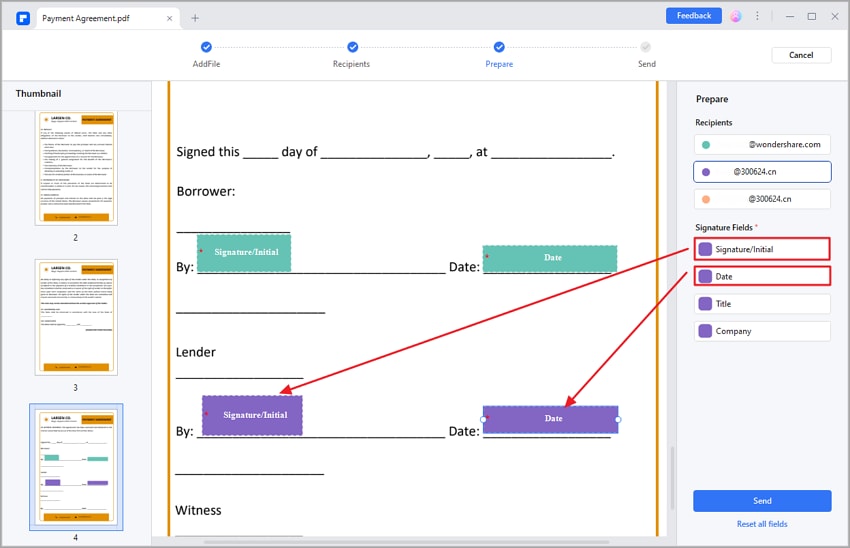
Step 3. Include signer fields in your PDFs.
- Add desired fields for signers to complete or sign within the document.
Step 4. Distribute files and monitor progress.
- Share the document with signers. Use the agreement tab to monitor signatures' status: sent, signed, or awaiting your signature.
For Basic Electronic Signatures, PDFelement enables users to add a simple electronic signature. This can be done by typing their name or selecting an "I agree" checkbox. This streamlines routine document signing tasks. It also eliminates the need for printing and scanning.
For Advanced Electronic Signatures, PDFelement ensures enhanced security. This is achieved through digital certificates, biometrics, and other authentication methods. Users can add a higher level of security to their signatures. This makes them suitable for critical contracts and sensitive agreements.
Moreover, for Qualified Electronic Signatures, PDFelement meets the stringent requirements. It meets specific regulations by incorporating government-approved certification authorities and digital certificates. This ensures the highest level of security and legal validity. Thus, making it ideal for high-value transactions and compliance-driven industries.
PDFelement meets the requirements of all three types of electronic signatures. It empowers businesses to streamline their signing processes and enhance document security. In the end, PDFelement offers a reliable electronic signature solution for various industries and use cases.
Conclusion
PDFelement emerges as a versatile and reliable electronic signature solution. Its eSign feature caters to various signature needs. This ranges from basic to qualified electronic signatures. PDFelement streamlines document management and enhances security. It was also equipped with a user-friendly interface and robust functionality. PDFelement is an ideal choice for businesses seeking an efficient electronic signature solution.
Free Download or Buy PDFelement right now!
Free Download or Buy PDFelement right now!
Buy PDFelement right now!
Buy PDFelement right now!
Up to 18% OFF: Choose the right plan for you and your team.
PDFelement for Individuals
Edit, print, convert, eSign, and protect PDFs on Windows PC or Mac.
PDFelement for Team
Give you the flexibility to provision, track and manage licensing across groups and teams.



Audrey Goodwin
chief Editor
Generally rated4.5(105participated)